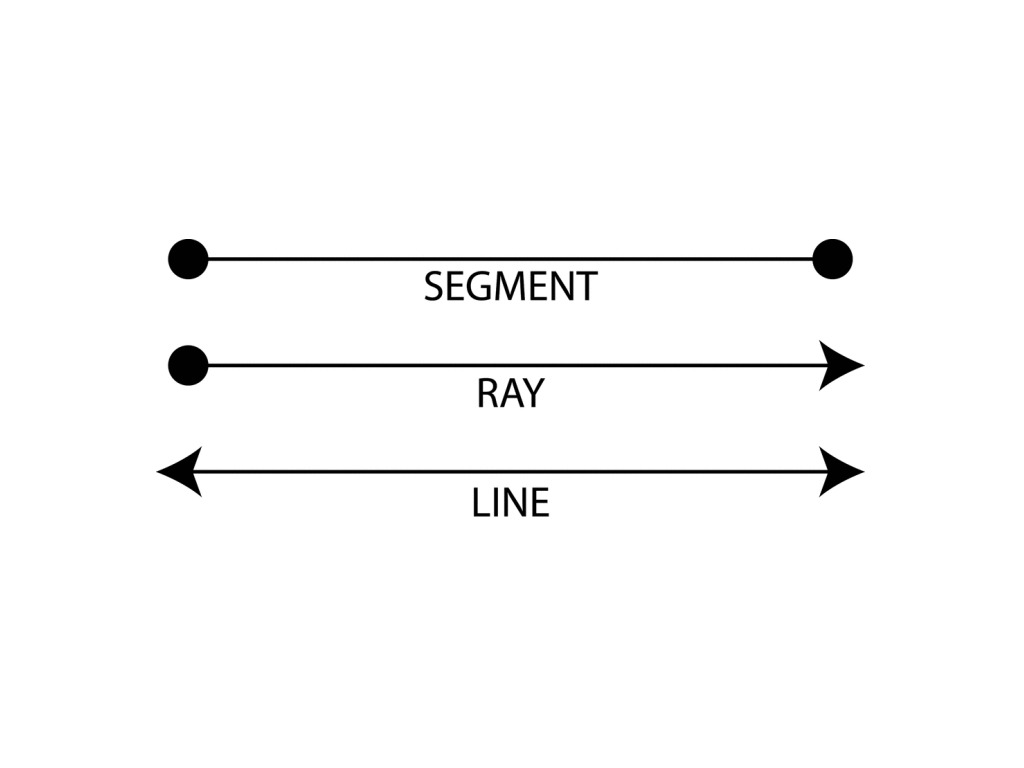
Geometry has always been considered to be one of the most complex subjects in mathematics. It has many branches such as linear algebra, plane geometry, solid geometry, and so on. But for now, let us just focus on a simple topic called ‘Ray’.
What is a ray?
A ray in geometry is simply any straight line that does not intersect itself. In other words, it is a line segment whose endpoints are both identical (ie. they coincide). For example, if we consider the figure below then the two rays AB and AC can be termed as “rays” since they do not meet at their ends.
So why is this concept important?
In the case of some geometric objects like circles, spheres, and polygons, the area enclosed by a given ray depends only on its starting point. Hence, when you study these shapes you will notice that all the points lying on the same ray form a closed shape having the same area.
- A ray is an imaginary line that is perpendicular to a line.
- A ray is a line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction parallel to the line.
- A ray is any line that begins at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction parallel to the line.
- A ray is a line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
- A ray is any line that starts at a point on a line and extends infinitely in a direction perpendicular to the line.
How to Use A Ray to Solve A Problem
You might have heard that the word “ray” is used in geometry. However, most of the time people don’t know how to apply these concepts. So, in this article, we’ll discuss the basics of using rays in geometry. Then, we will explain how you can use them to solve problems.
First, let’s start by explaining what a ray means. A ray is simply an imaginary line that extends from a point. If you want to understand more about it, then take a look at the diagram below.
In the picture above, you can see two points. The first one is the starting point. You could call that the origin of the ray. That would be the place where all of the lines in the figure begin.
The second point is the end of the ray. In other words, that is the point where the ray ends. This point is also known as the endpoint of the ray.
Now, here are some examples of what you can do with a ray.
- Find the length of any given segment.
- Calculate the area of any shape.
- Determine whether a given angle measures less than or greater than 90 degrees.
- Find the midpoint of a triangle.
- Find the distance between two points.
What Does A Ray Look Like?
A ray is a line that connects two points on the surface of a sphere. There are many different ways to describe a ray, but the most common way to define it is by saying that it goes from the center of the sphere to any point on the surface of the sphere.
There are three main kinds of rays. The first kind is called an interior ray. This type of ray starts at the center of the sphere and ends somewhere inside the sphere.
The second kind of ray is known as an exterior ray. An exterior ray begins outside the sphere and continues until it reaches the boundary of the sphere.
Finally, there is a third kind of ray, which is sometimes referred to as a “parallel” ray. A parallel ray passes through the center of the sphere, and then it extends outward in a straight line.
In geometry, the term “ray” can also refer to the distance between two points. For example, the distance between the North Pole and the South Pole is called the polar radius.
Importance of Rays in Geometry?
There are two main parts of geometry. One is angles and the other is lines. Angles include right angles, acute angles, obtuse angles, etc. Lines can be straight, curved, infinite, finite, closed, open, etc. The angle of a ray is equal to 180 degrees minus the sum of all the angles that make up the ray.
A line segment is made by connecting any two points on a line. A ray is formed when one point of a line is connected to infinity. For example, the rays from 0 to 1 and 0 to -1 are both segments. However, the ray from 0 to +∞ is not a segment.
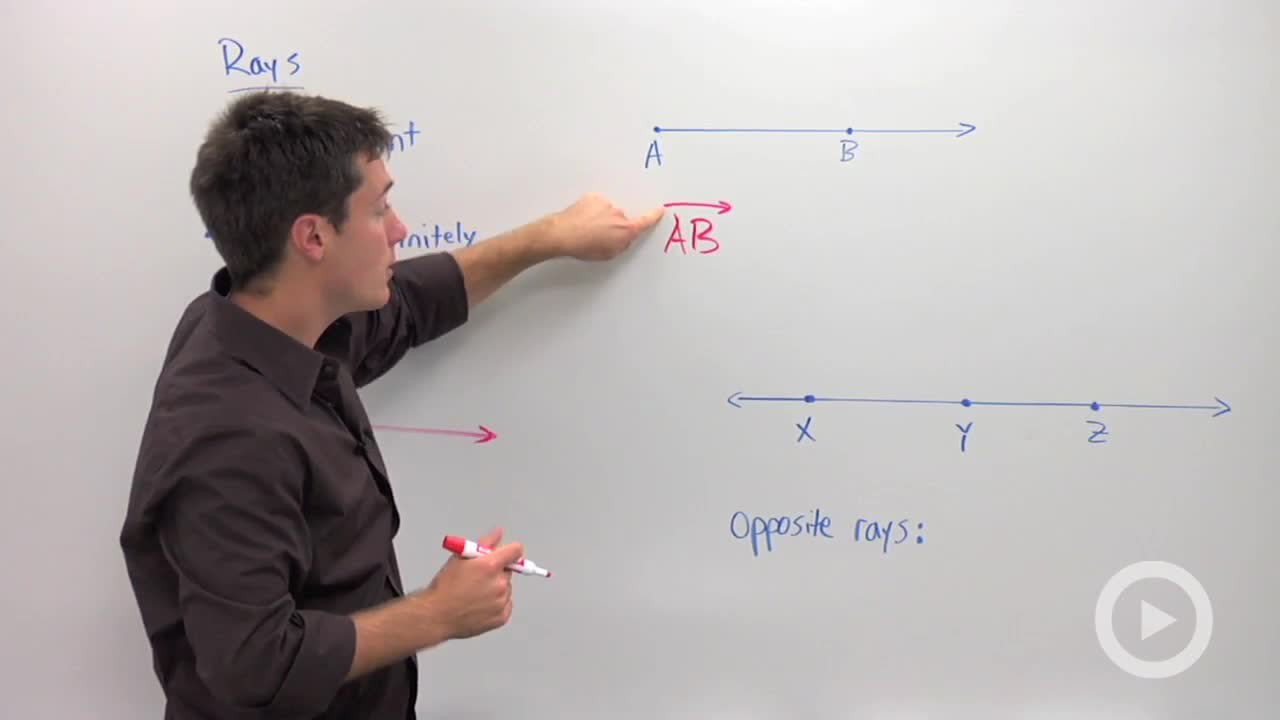
What Are the Different Types of Rays?
A ray is a line that extends infinitely in both directions from a point on a plane. The two most important properties of a ray are its length (measured in meters) and direction (a vector).
In geometry, you can use several tools to measure the lengths of lines. For example, you can draw your ruler, or you can buy one at any store. You can also use a protractor to measure angles between points.
There are three main kinds of rays: vertical, horizontal, and oblique.
Vertical rays extend vertically downward or upward. Horizontal rays go horizontally across the page. Oblique rays are angled concerning the x-axis or y-axis.
A horizontal ray is drawn in a perfectly horizontal position, starting from the point at which you click on the chart to place the tool, and moving forward in time.
Lines, segments, or rays that intersect at any angle other than 90° are called oblique.
How Can You Use a Ray in Geometry?
A ray of light is a line that extends infinitely from a point. For example, the sun’s rays extend forever. The angle between two parallel lines is 90 degrees. This means that they intersect at right angles. A straightedge is any tool used to draw perpendicular lines. When you have a ruler, it can be used to measure angles and lengths.
In geometry, a ray of light can also be used as an imaginary extension of a line. In this case, the ray represents the length of the line. If you look closely at the picture below, you’ll notice that a ray has been drawn extending outwards from the top of the page.
Here are some examples of how you can use rays in geometry:
- Find the area of a circle using a radius and a diameter.
- Draw the sides of a triangle given the three angles.
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle.
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the distance of a hypotenuse.
- Determine whether or not two triangles are similar.
- Determine whether or not a parallelogram is a rhombus.
- Figure out if a quadrilateral is convex or concave.
- Check for symmetry in a polygon.

 Lucas Green
Lucas Green